🛠️ Interaction Modes
CodeGPT offers three distinct modes to interact with AI, each optimized for different types of development tasks. You can switch between these modes using the selector at the bottom of the chat panel.

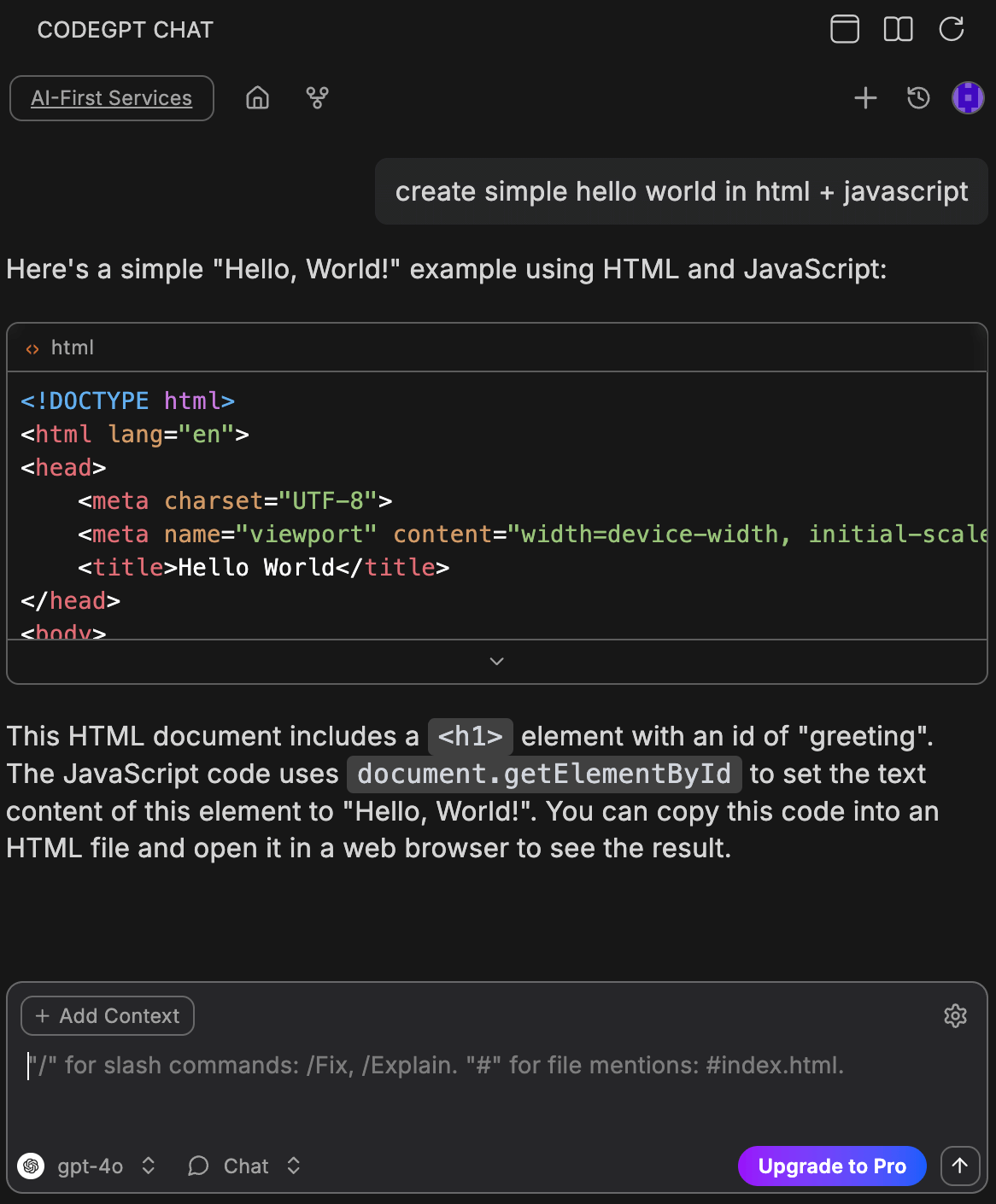
💬 Chat Mode
Ideal for: General questions, explanations, and quick code snippets.
- Works like a standard conversational interface.
- Maintains short-term history of the current conversation.
- Best for "How do I use this library?" or "Explain this function."
🔍 Search Mode
Ideal for: Finding specific information across your codebase or online.
- Uses the Augmented Context (if indexed) to locate logic.
- Optimized for retrieval tasks.
- Best for "Where is the API endpoint for users defined?" or "Find all usages of the deprecated logger."
🤖 Agent Mode
Ideal for: Complex, multi-step tasks and autonomous problem-solving.
- The Agent can think and execute multiple steps to solve a goal.
- It can read files, write code, and even suggest terminal commands.
- Best for "Create a new React component that handles a login form with validation" or "Refactor the entire networking layer to use Axios instead of Fetch."
- Note: Agent mode is more powerful but may consume more tokens as it performs multiple turns of reasoning.
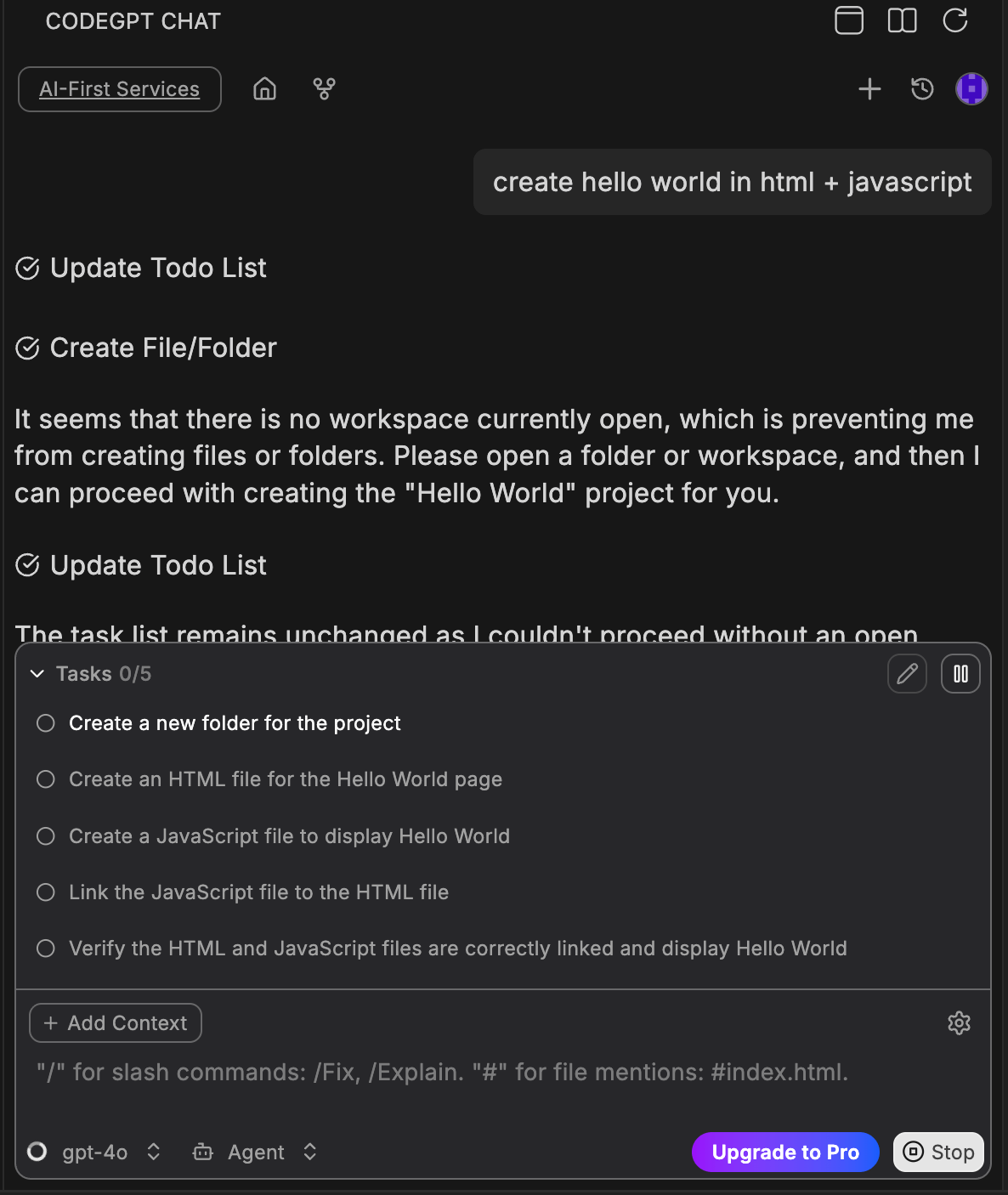
Task Planning
When using Agent mode, CodeGPT creates a task list to organize and execute complex requests step by step.
🚀 Switching Modes
At the bottom of the CodeGPT panel, next to the model selector, you'll find the Mode Selector. Simply click it to toggle between Chat, Search, and Agent depending on your needs.
⚡ Quick Actions
CodeGPT provides powerful quick actions that you can access by right-clicking on selected code or through the command palette. These actions help you perform common tasks instantly.
📖 Explain CodeGPT
What it does: Provides a detailed explanation of the selected code, breaking down its logic and purpose.
Example use case:
// You have this complex regex and need to understand it:
const emailRegex = /^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$/;
// Select the line → Right-click → "Explain CodeGPT"
// Result: CodeGPT explains each part of the regex pattern🔄 Refactor CodeGPT
What it does: Suggests improvements to your code structure, readability, and performance.
Example use case:
// Before refactoring:
function getData(id) {
let result = null;
if (id !== null && id !== undefined) {
result = fetch('/api/' + id).then(r => r.json());
}
return result;
}
// Select → "Refactor CodeGPT" → Get cleaner version:
const getData = async (id) => {
if (!id) return null;
const response = await fetch(`/api/${id}`);
return response.json();
};💬 Comment Code CodeGPT
What it does: Automatically adds inline comments explaining what each part of your code does.
Example use case:
// Before:
function fibonacci(n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
// After "Comment Code CodeGPT":
// Calculates the nth Fibonacci number using recursion
function fibonacci(n) {
// Base case: return n if it's 0 or 1
if (n <= 1) return n;
// Recursive case: sum of previous two Fibonacci numbers
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}📝 Document CodeGPT
What it does: Generates comprehensive documentation (JSDoc, docstrings, etc.) for your functions and classes.
Example use case:
// Before:
function calculateDiscount(price, percentage, maxDiscount) {
const discount = price * (percentage / 100);
return Math.min(discount, maxDiscount);
}
// After "Document CodeGPT":
/**
* Calculates a discount amount based on price and percentage.
* @param {number} price - The original price of the item
* @param {number} percentage - The discount percentage to apply
* @param {number} maxDiscount - Maximum discount amount allowed
* @returns {number} The calculated discount, capped at maxDiscount
* @example
* calculateDiscount(100, 20, 15) // Returns 15 (capped)
* calculateDiscount(100, 10, 15) // Returns 10
*/
function calculateDiscount(price, percentage, maxDiscount) {
const discount = price * (percentage / 100);
return Math.min(discount, maxDiscount);
}🔧 Fix this with CodeGPT
What it does: Identifies bugs or errors in your code and suggests fixes.
Example use case:
// Code with a bug:
function getAverage(numbers) {
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= numbers.length; i++) { // Bug: should be < not <=
sum += numbers[i];
}
return sum / numbers.length;
}
// "Fix this with CodeGPT" identifies the off-by-one error:
function getAverage(numbers) {
if (!numbers?.length) return 0; // Also adds null check
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) { // Fixed!
sum += numbers[i];
}
return sum / numbers.length;
}🧪 Unit Test
What it does: Generates unit tests for your selected function or class.
Example use case:
// Your function:
function isPalindrome(str) {
const cleaned = str.toLowerCase().replace(/[^a-z0-9]/g, '');
return cleaned === cleaned.split('').reverse().join('');
}
// "Unit Test" generates tests:
describe('isPalindrome', () => {
test('returns true for simple palindrome', () => {
expect(isPalindrome('racecar')).toBe(true);
});
test('returns true for palindrome with spaces', () => {
expect(isPalindrome('A man a plan a canal Panama')).toBe(true);
});
test('returns false for non-palindrome', () => {
expect(isPalindrome('hello')).toBe(false);
});
test('handles empty string', () => {
expect(isPalindrome('')).toBe(true);
});
});💡 How to Use Quick Actions
- Select the code you want to transform
- Right-click to open the context menu
- Choose the action from the CodeGPT submenu
- Review the result in the chat panel or inline
You can also access these actions via the Command Palette (Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + P) by typing "CodeGPT".
🔜 Next Step
Learn how to manually provide context using the Add Context Tool.